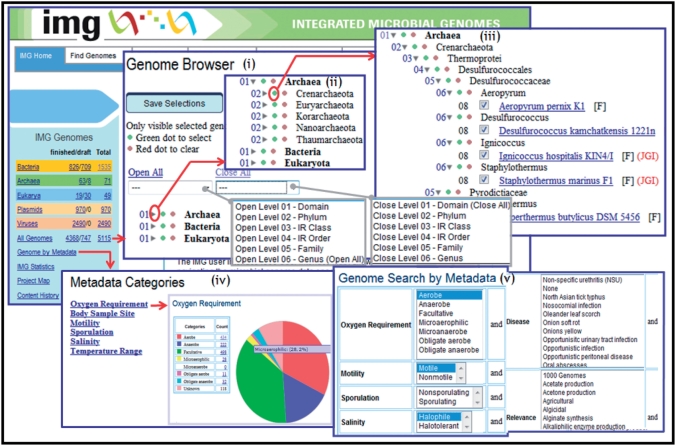
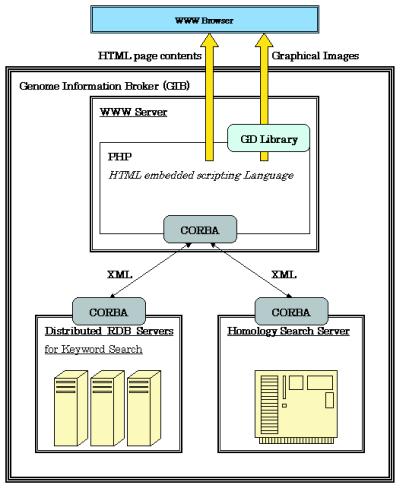
Genome Information Broker (GIB) is a robust device for the research of comparative genomics. GIB permits customers to retrieve and show partial and/or complete genome sequences along with the related organic annotation.
GIB has gathered all of the completed microbial genome and has not too long ago been expanded to incorporate Arabidopsis thaliana genome data from DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank. In the close to future, lots of of genome sequences shall be decided.
In order to deal with such big data, we’ve got enhanced the GIB structure through the use of XML, CORBA and distributed RDBs. We introduce the brand new GIB right here.
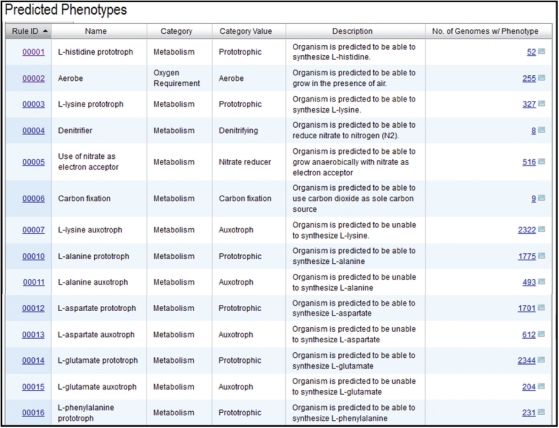
The built-in microbial genomes (IMG) system in 2007: data content material and analysis device extensions.
The built-in microbial genomes (IMG) system is a data administration, analysis and annotation platform for all publicly out there genomes. IMG comprises each draft and full JGI microbial genomes built-in with all different publicly out there genomes from all three domains of life, along with numerous plasmids and viruses.
IMG gives instruments and viewers for analyzing and annotating genomes, genes and capabilities, individually or in a comparative context. Since its first launch in 2005, IMG’s data content material and analytical capabilities have been consistently expanded via quarterly releases. IMG is supplied by the DOE-Joint Genome Institute (JGI )
Molecular signatures of sepsis: multiorgan gene expression profiles of systemic irritation.
During sepsis the host’s system-wide response to microbial invasion appears dysregulated. Here we discover the varied multiorgan transcriptional applications activated throughout systemic irritation in a cecal ligation/puncture mannequin of sepsis in rats. Using DNA microarrays representing 7398 genes, we examined the temporal sequence of sepsis-induced gene expression patterns in main organ methods together with lung, liver, kidney, thymus, spleen, and mind.
Although genes recognized to be related to systemic irritation have been recognized by our world transcript analysis, many genes and expressed sequence tags not beforehand linked to the septic response have been additionally elucidated. Taken collectively, our outcomes recommend activation of a extremely complicated transcriptional response in particular person organs of the septic animal. Several overlying themes emerged from our genome-scale analysis that features
1) the sepsis response elicited gene expression profiles that have been both organ-specific, frequent to a couple of organ, or distinctly reverse in some organs; 2) the mind is protected against sepsis-induced gene activation relative to different organs; 3) the thymus and spleen have an attention-grabbing cohort of genes with opposing gene expression patterns; 4) genes with proinflammatory results have been usually balanced by genes with anti-inflammatory results (eg, interleukin-1beta/decoy receptor, xanthine oxidase/superoxide dismutase, Ca2+-dependent PLA2/Ca2+-independent PLA2); and 5) differential gene expression was noticed in proteins accountable for stopping tissue damage and selling homeostasis together with anti-proteases (TIMP-1, Cpi-26), oxidant neutralizing enzymes (metallothionein), cytokine decoy receptors (interleukin-1RII), and tissue/vascular permeability components (aquaporin 5, vascular endothelial progress issue).
This world perspective of the sepsis response ought to present a molecular framework for future analysis into the pathophysiology of systemic irritation. Understanding, on a genome scale, how an organism responds to an infection, might facilitate the event of enhanced detection and therapy modalities for sepsis.